Gum Growth Near Back Tooth: Causes, Treatment, and Healing Timeline
What Is Seen in This Case?
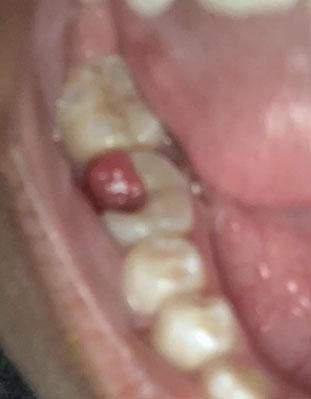
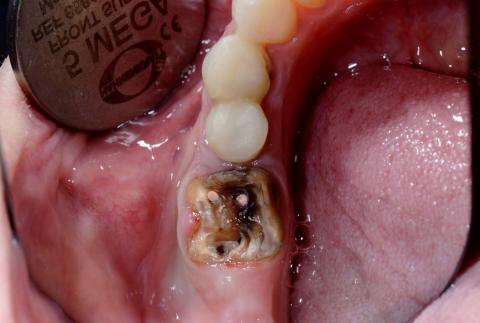
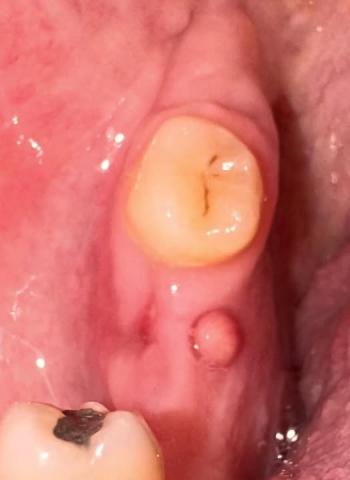
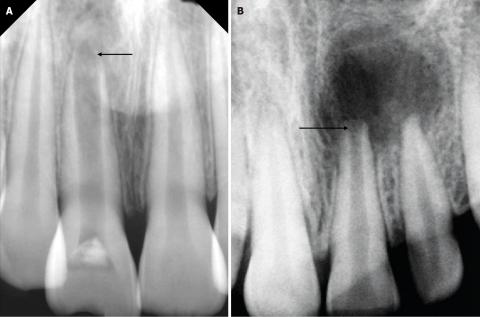
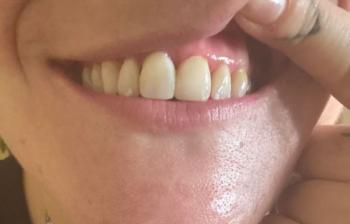
The image shows a red, swollen growth on the gum near a back tooth (molar). The surrounding tooth appears intact, but the gum tissue is inflamed and raised. This type of lesion is commonly associated with local infection, irritation, or gum overgrowth.
This condition should not be ignored, even if pain is mild.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual examination, the most likely conditions include:
-
Localized gum infection
-
Gingival abscess