7-Day Post-Extraction Check: Deep Socket but No Pain - Normal Healing or Dental Risk?
Quick visual impression (100% / zoom)
-
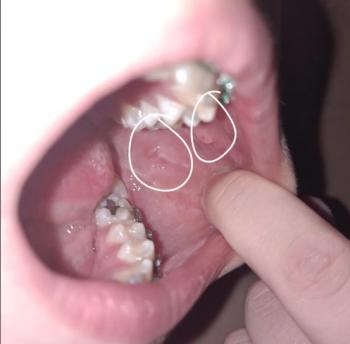
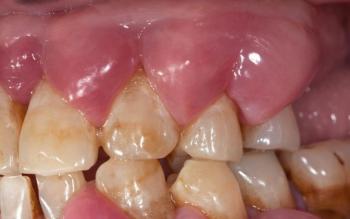
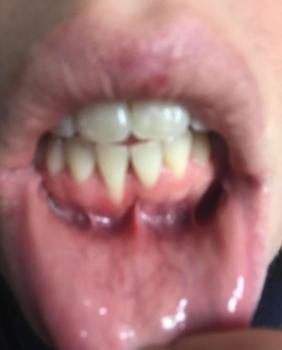
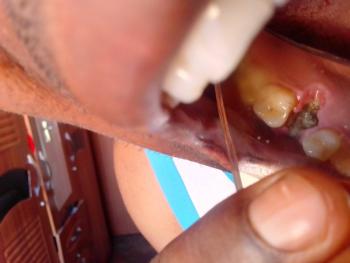
I see a dark, fairly deep socket behind the last visible molar (the extraction site).
-
No obvious pus or large swelling visible in the photo and you report no pain — both reassuring.
-
Surrounding teeth look intact. Photo lighting/angle limits how much I can see (I can’t check bleeding under the gum or feel for mobility).