Dentures That Feel Natural, Look Beautiful.
Deep Interproximal Cavities & Restorations: Immediate Treatment Plan + 14-Day Recovery Guide
Language :
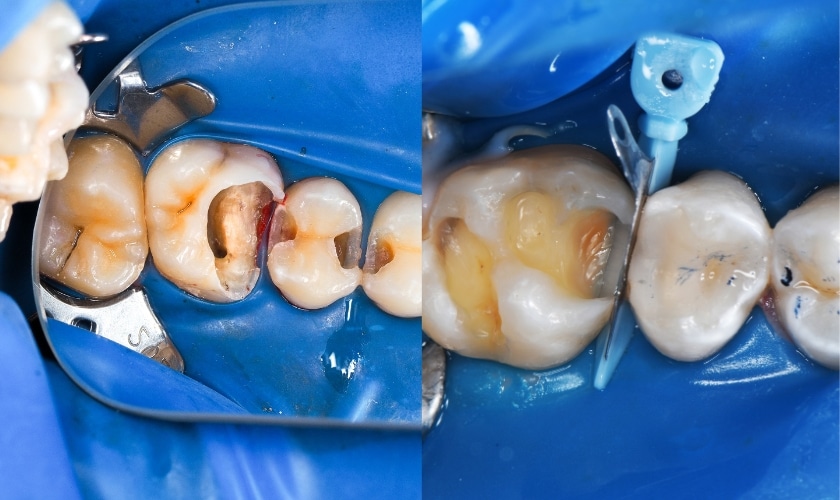
Full analysis & diagnosis (Zoom 100%)
-
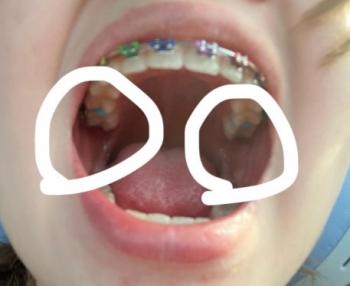
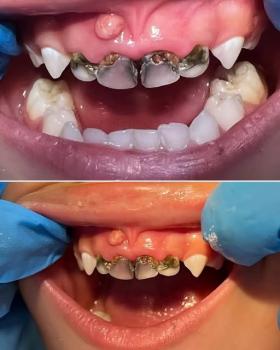
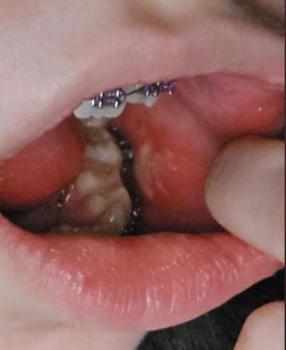
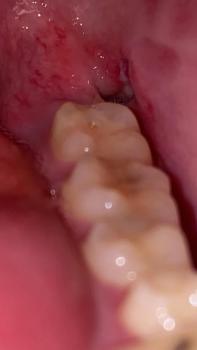
Findings from the images: Rubber dam isolation with matrix bands in place; multiple deep occlusal-/proximal caries excavations on posterior teeth. Some restorations are in progress — there is close proximity to the pulp on at least one surface. Tooth structure shows large cavities with thin remaining walls.
-
Most likely diagnosis: Moderate → deep dental caries (proximal and occlusal) with very high risk of pulpal involvement. One or more teeth may have reversible or irreversible pulpitis depending on symptoms and whether the pulp has been exposed during excavation.
-
Clinical signs to check (if onsite): spontaneous pain, prolonged thermal sensitivity, percussion tenderness, swelling, sinus tract, mobility, and periapical tenderness.
Examine deeply — recommended immediate tests & imaging
-
Periapical radiographs (or bitewing + periapical) to assess depth of decay and periapical status.
-
Pulp vitality testing (cold, EPT) to determine pulp health.
-
Percussion and palpation tests.
-
Inspect for pulp exposure once caries fully removed.
Process to execute (step-by-step plan)
-
Complete assessment & consent — explain options and risks.
-
Isolation & caries removal (rubber dam already placed in images) — remove infected dentin, preserve sound tooth structure.
-
Pulp management:
-
If no pulp exposure and pulp tests indicate vitality → place liner (calcium hydroxide or MTA if very near pulp) and proceed with definitive restoration (composite/indirect onlay)
-
If pulp exposure or signs of irreversible pulpitis/periapical pathology → root canal treatment (RCT) is indicated before final restoration.
-
-
Restoration: restore with appropriate material (composite resin, ceramic onlays or full coverage if cusp involvement) and re-establish proper contact/occlusion. Use matrix for proximal contacts as shown.
-
Occlusal adjustment and finish/polish.
-
Post-op instructions and analgesics ± antibiotics (only if systemic signs or spreading infection).
-
Follow-up at 7 days and 6–8 weeks (radiograph if RCT performed or edema/persistent symptoms).
Time frame to heal (if treatment performed now)
-
Immediate pain relief: often within 24–72 hours after appropriate treatment and analgesics.
-
Short term (7–14 days): soft-tissue healing, resolution of acute symptoms; temporary sensitivity may persist.
-
14 days scenario: if RCT not required and definitive restoration placed, patient should be comfortable with reduced sensitivity. If RCT performed, initial healing and symptom control usually within 7–14 days; complete periapical healing takes months.
-
Full restoration integration & monitoring: depending on complexity, 2–6 weeks for final adjustments and monitoring; radiographic healing if infection present will be longer (months).
What will scale up if ignored (risks of delay)
-
Progression to irreversible pulpitis → pulpal necrosis.
-
Development of periapical abscess, facial swelling, sinus tract.
-
Spread of infection to bone (osteomyelitis) or systemic (rare but possible).
-
Increased tooth structure loss → fracture → need for extraction.
-
More complex, costly treatment (extraction + implant or bridge) rather than a restoration or RCT.
Short actionable advice for patient (today)
-
Avoid chewing on the affected side.
-
Take recommended analgesics (e.g., paracetamol/ibuprofen per label or dentist prescription).
-
Keep area clean with gentle rinses (warm saline).
-
Seek urgent dental evaluation — do not wait if pain is severe, swelling present, or fever occurs.
Comments
Current images show appropriate isolation and restorative technique underway — this is good practice. However, because cavities are deep and very close to the pulp, careful pulp assessment is critical. If the pulp was exposed during excavation, immediate pulpal treatment (direct pulp capping only if small exposure in a young tooth and conditions ideal) or RCT is needed. Conservative care prevents escalation to extraction.
Visit nearest dental clinic
Find local clinics and emergency dental care here:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic